Digital FD-8 pedal
From Just in Time
[[Revision timestamp::20140329001303|]] In Roland FD-8 Issues: Hall Sensor Modification we described how a ratiometric hall sensor could replace the resistor film to repair the Roland FD-8 high hat pedals. Even though that Hall Sensor implementation works, an MCU based approach might have some additional advantages:
- complete variable resistance to be compatible with other drum modules
- adjustable sensitivity curve
- more than 3 resistor levels, allowing true detection of foot-down velocity.
- auto-calibration, i.e. no need for pots to set the trigger points.
Electronics
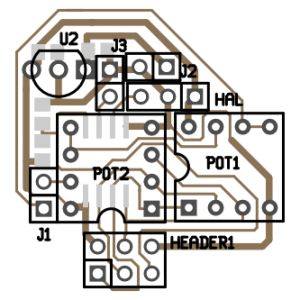
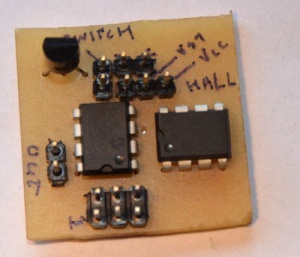
The microcontroller-based version offers 256 different pedal positions at a BOM cost that is still much lower than $10. The components used are:
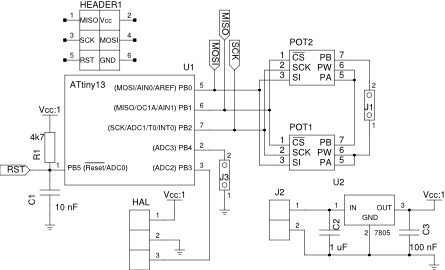
- One SMT attiny13 MCU (ebay, datasheet), an 8-pin AVR with effectively 5 io pins and 10-bit ADC;
- Two MCP41010 digital potentiometers (ebay, datasheet) in series to emulate the film resistor in the FD-8. We need a range of approximately 0-20K and while the 10K MCP41010 is readily available on ebay, we had trouble finding a cost-effective 20K or 50K digital pot. Hence the two pots in series;
- One Honeywell SS490 ratiometric hall effect sensor as in the non-MCU version, or alternatively an Allegro A1302 (Just ordered a pair on ebay). The latter should be comparable to the Honeywell if used in a 5V setup, but this hasn't been tested yet;
- Any old 78L05 that we can get our hands on;
- an SMT resistor and several SMT capacitors.
Pin PB4 is currently not used, but is connected to a header on the print, so that a (momentary) switch could be connected. The idea is that currently the pedal will have to calibrate every time it switches on (determining the range of the pedal), but it would be possible to write the calibrated values to eeprom. The switch can then be used to trigger a reset of the calibrated values. Alternatively, the switch could be used to set set the 'half-closed' point of the pedal.
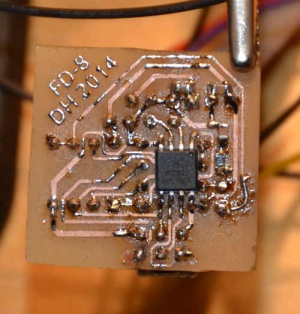
Because this is a prototype, there is still a 6-pin header on the PCB to reflash firmware. The PCB is designed in such a way that the header can be removed (sawn off) without re-routing. If at some point a single potmeter version would be feasible (using for instance an MCP41050), the second potmeter can also be removed with minimal re-routing. This would result in a much smaller PCB.
An svg-file of the PCB traces that is ready for toner transfer can be found here.
Build
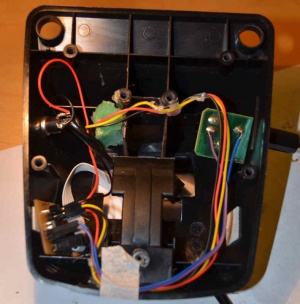
Mechanically, the build is very similar to the comparator-based one. This time around the PCB is somewhat bigger and the leads to the sensor were a bit longer, making it harder to cleanly place everything inside the enclosure. Some hot glue helped in keeping the wires out of the way while assembling the pedal. Because I wasn't so sure about the correct height for the sensor, I just glued it to a sponge and glued the sponge into the housing. This avoids damaging the sensor with an over-enthousiastic stomp.
Just as with the comparator based version, the electronics need their own power supply and for that purpose a socket was added to the pedal housing. Power to the drum computer is then provided through a cable running from the pedal.
Software
The software for this device is available on GitHub.
The basic mode of operation is as follows:
- Measure the output voltage of the hall sensor using the ADC.
- Determine a corresponding resistance and program that resistance value in the digital pots.
- Repeat
There are two complexities that the firmware resolves as it performs the above two steps:
- Range. Depending on the strength of the magnet and its distance from the sensor, the Hall effect sensor will report only a limited range of values that don't span the complete possible range. The firmware will detect the minimum and maximum values and use those to map that range to the full range of 0—255 that should be given to the potentiometer;
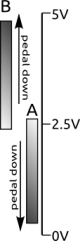
- Polarity. Ratiometric Hall effect sensors typically output a voltage of ½Vcc if no magnetic field is sensed. As soon as a magnet approaches, the voltage will either go up towards Vcc (case B in the image to the right) or down towards Vss (A in the image), depending on the orientation of the magnet. The magnet approaches the sensor as the pedal is moved down. The firmware will autodetect the direction of "pedal down" by determining the middle of the measured range.
All of that is contained in one single source file.